Medical procurement leaders are facing pressure to deliver revenue amidst unprecedented challenges. Supply chain issues, staffing shortages, and a high focus on value-based healthcare can make you feel like you’re being asked to deliver the impossible.
We hear you, and we can help.LOWERING COST OF CARE THROUGH MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
We are helping facilities harness the power of low pressure to increase procedural efficiency, reduce length of stay, and impact their cost of care with AirSeal® - regardless of if your surgeons are using a robotic or traditional laparoscopic approach.
Post-operative metrics show operating at low pressure with AirSeal® delivers:
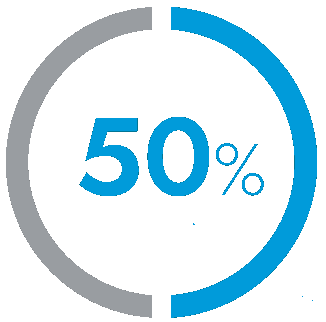
Reduction
in hospital length of stay1-8
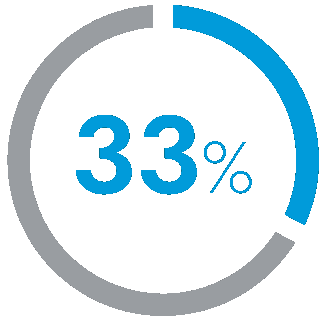
Reduction
in PACU length of stay1-8
RONNEY ABAZA, MD
UrologyLOS Reduction of 0.43 days = +$1,360
BRUCE RAMSHAW, MD
General, HerniaLOS Reduction of 1.5 days = +$3,944
QUENTIN DENOST, MD PhD
ColorectalLOS Reduction of 1 day = +$2,883*
DANA TALEM, MD
General, GallbladderLOS Reduction of 10 hours = +$995
KATHY HUANG, MD
GynecologyLOS Reduction of 2 hours = +$301
VEDRA AUGENSTEIN, MD
General, HerniaLOS Reduction of 1.4 days = +$3,602
* Based on Hospital Adjusted Expenses per Inpatient Day in US
to impact procedures and outcomes.
36
Peer-Reviewed Studies
5
Surgical Specialties
7.5M+
Procedures
4,000
Facilities
80
Countries
PATIENT BENEFITS
Recently published clinical studies using AirSeal® at low pressure have also concluded:

Reduction in Postoperative Pain Scores1-8

Improved Respiratory Parameters2,3,10-15

Decreased Complications & 30-day Readmissions4,13,14,16-20
AirSeal® iFS is the innovative insufflator transforming laparoscopic procedures and outcomes.
By delivering stable, consistent pnuemo and smoke evacuation, AirSeal provides your patients the benefits of operating at low pressure with AirSeal® including reducing length of stay.
“If patients feel better after their operation, we’re able to send them home. If our recovery rooms are full then we can’t move on to the next patient. And so, it helps the hospital and everyone overall if we can get the patients home faster.”


Dr. Bahareh M. Nejad
Director of Robotic Surgery and Clinical Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
1 Ramshaw B, Forman B, Heidel E, Dean J, Gamenthaler A, Fabian M. A Clinical Quality Improvement (CQI) Project to Improve Pain After Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair. Surg Technol Int. 2016;29:125-130.
2 Foley CE, Ryan E, Huang JQ. Less is more: clinical impact of decreasing pneumoperitoneum pressures during robotic surgery. J Robot Surg. 2021;15(2):299- 307. doi:10.1007/s11701-020-01104-4c
3 Saway JP, McCaul M, Mulekar MS, McMahon DP, Richards WO. Review of Outcomes of Low Verses Standard Pressure Pneumoperitoneum in Laparoscopic Surgery. Am Surg. 2022;88(8):1832-1837. doi:10.1177/00031348221084956
4 Buda A, Di Martino G, Borghese M, et al. Low-Pressure Laparoscopy Using the AirSeal System versus Standard Insufflation in Early-Stage Endometrial Cancer: A Multicenter, Retrospective Study (ARIEL Study). Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10(3):531. Published 2022 Mar 14. doi:10.3390/healthcare10030531
5 Ferroni MC, Abaza R. Feasibility of robot-assisted prostatectomy performed at ultra-low pneumoperitoneum pressure of 6 mmHg and comparison of clinical outcomes vs standard pressure of 15 mmHg. BJU Int. 2019;124(2):308-313. doi:10.1111/bju.14682
6 Ramshaw B, Vetrano V, Jagadish M, Forman B, Heidel E, Mancini M. Laparoscopic approach for the treatment of chronic groin pain after inguinal hernia repair : Laparoscopic approach for inguinodynia. Surg Endosc. 2017;31(12):5267-5274. doi:10.1007/s00464-017-5600-3
7 Abaza R, Martinez O, Ferroni MC, Bsatee A, Gerhard RS. Same Day Discharge after Robotic Radical Prostatectomy. J Urol. 2019;202(5):959-963. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000000353
8 Celarier S, Monziols S, Célérier B, et al. Low-pressure versus standard pressure laparoscopic colorectal surgery (PAROS trial): a phase III randomized controlled trial. Br J Surg. 2021;108(8):998-1005. doi:10.1093/bjs/znab069
9 Data on file according to Kaiser Family Foundation Cost per Day 2021 by state for for-profit hospitals
10 Bucur P, Hofmann M, Menhadji A, et al. Comparison of Pneumoperitoneum Stability Between a Valveless Trocar System and Conventional Insufflation: A Prospective Randomized Trial. Urology. 2016;94:274-280. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2016.04.022
11 Covotta M, Claroni C, Torregiani G, et al. A Prospective, Randomized, Clinical Trial on the Effects of a Valveless Trocar on Respiratory Mechanics During
12 Robotic Radical Cystectomy: A Pilot Study. Anesth Analg. 2017;124(6):1794-1801. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002027
13 Abaza R, Ferroni MC. Randomized Trial of Ultralow vs Standard Pneumoperitoneum during Robotic Prostatectomy. J Urol. 2022;208(3):626-632. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002729
14 Sroussi J, Elies A, Rigouzzo A, et al. Low pressure gynecological laparoscopy (7mmHg) with AirSeal® System versus a standard insufflation (15mmHg): A pilot study in 60 patients. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2017;46(2):155-158. doi:10.1016/j.jogoh.2016.09.003
15 Buda A, Di Martino G, Borghese M, et al. Low-Pressure Laparoscopy Using the AirSeal System versus Standard Insufflation in Early-Stage Endometrial Cancer:A Multicenter, Retrospective Study (ARIEL Study). Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10(3):531. Published 2022 Mar 14. doi:10.3390/healthcare10030531
16 Feng TS, Heulitt G, Islam A, Porter JR. Comparison of valve-less and standard insufflation on pneumoperitoneum-related complications in robotic partial nephrectomy: a prospective randomized trial. J Robot Surg. 2021;15(3):381-388.
17 Desroches B, Porter J, Bhayani S, Figenshau R, Liu PY, Stifelman M. Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy of Valveless and Standard Insufflation During Robotic Partial Nephrectomy: A Prospective, Randomized, Multi-institutional Trial. Urology. 2021;153:185-191. doi:10.1016/j.urology.221.01.047 doi:10.1007/s11701-020-01117-z
18 Rohloff M, Cicic A, Christensen C, Maatman TK, Lindberg J, Maatman TJ. Reduction in postoperative ileus rates utilizing lower pressure pneumoperitoneum in robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Robot Surg. 2019;13(5):671-674. doi:10.1007/s11701-018-00915-w
19Grieco M, Tirelli F, Agnes A, Santocchi P, Biondi A, Persiani R. High-pressure CO2 insufflation is a risk factor for postoperative ileus in patients undergoing TaTME. Updates Surg. 2021;73(6):2181-2187. doi:10.1007/s13304-021-01043-1
20Annino F, Topazio L, Autieri D, Verdacchi T, De Angelis M, Asimakopoulos AD. Robotic partial nephrectomy performed with Airseal versus a standard CO2 pressure pneumoperitoneum insufflator: a prospective comparative study. Surg Endosc. 2017;31(4):1583-1590. doi:10.1007/s00464-